Research
Postdoc
During my first year as a postdoc, I worked as a research fellow at the italian National Research Center (CNR-IEIIT): my activity led to a contribution to the development of the Interomics flagship project as well as to innovative extensions of the Rulex machine learning software suite. After that, I joined the Rulex company, becoming the Head of Data Science in March 2019.
Rulex
The Rulex software suite is a prescriptive analytics machine learning platform, comprising both ETL tools, well-known and propertary, exclusive machine learning algorithms, such as the Logic Learning Machine.
My contributions to the suite, included in the official release since the 3.2 version, concern, for instance, the development of both the front-end and the back-end of tasks in the area of association rules mining. The back-end was developed in C++, while the GUI is Python-based. Together with the implementation of well-established techniques such as the Eclat algorithm, the development of innovative tools, especially oriented towards complexity reduction and assortment optimization was also addressed.
Reference papers:
A Novel Rule-Based Modeling and Control Approach for the Optimization of Complex Water Distribution Networks, Enrico Ferrari, Damiano Verda, Nicolò Pinna, Marco Muselli, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Springer 2023
Validation of a predictive model for obstructive sleep apnea in people with Down syndrome, Brian G. Skotko, Alexandra Garza Flores, Ibrahim Elsharkawi, Vasiliki Patsiogiannis, Mary Ellen McDonough, Damiano Verda, Marco Muselli, Roberto Hornero, David Gozal, Eric A. Macklin, American Journal Of Medical Genetics, Part A, November 2022
The clinical meaning of the area under a Receiver Operating Characteristic curve for the evaluation of the performance of disease markers, Stefano Parodi, Damiano Verda, Francesca Bagnasco, Marco Muselli, Epidemiology And Health, October 2022
LLM-PBC: Logic Learning Machine-Based Explainable Rules Accurately Stratify the Genetic Risk of Primary Biliary Cholangitis, Alessio Gerussi, Damiano Verda, Claudio Cappadona, Laura Cristoferi, Davide Paolo Bernasconi, Sandro Bottaro, Marco Carbone, Marco Muselli, Pietro Invernizzi, and Rosanna Asselta on behalf of The Italian PBC Genetics Study Group, Journal of Personalized Medicine, September 2022
Machine learning in primary biliary cholangitis: A novel approach for risk stratification , Alessio Gerussi, Damiano Verda, Davide Paolo Bernasconi, Marco Carbone, Atsumasa Komori, Masanori Abe, Mie Inao, Tadashi Namisaki, Satoshi Mochida, Hitoshi Yoshiji, Gideon Hirschfield, Keith Lindor, Albert Pares, Christophe Corpechot, Nora Cazzagon, Annarosa Floreani, Marco Marzioni, Domenico Alvaro, Umberto Vespasiani-Gentilucci, Laura Cristoferi, Maria Grazia Valsecchi, Marco Muselli, Bettina E. Hansen, Atsushi Tanaka, Pietro Invernizzi, Liver International, Issue Cover March 2022
Controllo automatico delle variabili cliniche della scheda di dimissione ospedaliera (SDO), mediante l’utilizzo di tecniche di machine learning (in Italian language), E. Montel, A. Richter, R. Vanzetta, S. Ladurner, A. Malizia, D. Verda, M. Muselli, P. Santin, P. Vian, Organizzazione Sanitaria, Marzo 2022
A New XAI-based Evaluation of Generative Adversarial Networks for IMU Data Augmentation, Sara Narteni, Vanessa Orani, Enrico Ferrari, Damiano Verda, Enrico Cambiaso, Maurizio Mongelli, IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application and Services (HealthCom) 2022
Interomics
The Interomics Flagship project is oriented towards the development of an integrated platform for the application of "omic" sciences to biomarker definition and theranostic, predictive and diagnostic profiles.
Reference papers:
Analyzing gene expression data for pediatric and adult cancer diagnosis using logic learning machine and standard supervised methods , Damiano Verda, Stefano Parodi, Enrico Ferrari, Marco Muselli, BMC Bioinformatics, November 2019
Logic Learning Machine and standard supervised methods for Hodgkin’s lymphoma prognosis using gene expression data and clinical variables , Stefano Parodi, Chiara Manneschi, Damiano Verda, Enrico Ferrari, Marco Muselli, Health Informatics Journal, March 2018
PhD
During the PhD, my research activity focused on robotic perception. More specifically, I worked on three projects, briefly described in the following, which make use of a laser scanner, a Microsoft Kinect and a camera. All these sensors are used in robotics, given that each of them exhibits both desirable features and downsides:
- a laser scanner ensures to get a fixed number of reliable distance measurements, but it gathers these measurements only on the scanning plane and it is limited by a maximum distance range,
- a camera is not affected by any of these restrictions, but the perceived image requires computation in order to be associated to a (variable) amount of recognizable features,
- the Microsoft Kinect is strongly limited by its maximum scanning range (4m) and cannot be reliably used outdoor (given its sensitivity to lighting conditions), but it is a low-cost sensor providing 3D data.
Micro Air Vehicle (MAV) position tracking
During the period I spent at the Robotics and Perception Group at the University of Zurich (led by prof. Davide Scaramuzza) I contributed to the development of a purely vision-based position tracking technique for Micro Air Vehicles (MAVs).

Reference papers:
Air-ground Matching: Appearance-based GPS-denied Urban Localization of Micro Aerial Vehicles, Andràs L. Majdik, Damiano Verda, Yves Albers-Schoenberg, Davide Scaramuzza, Journal of Field Robotics (JFR), October 2015
Micro Air Vehicle Localization and Position Tracking from Textured 3D Cadastral Models, Andràs L. Majdik, Damiano Verda, Yves Albers-Schoenberg, Davide Scaramuzza, International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2014
Structure-based object category recognition
A Microsoft Kinect sensor is used as an input for an object category recognition application, the Kinect is mounted on a ground robot.
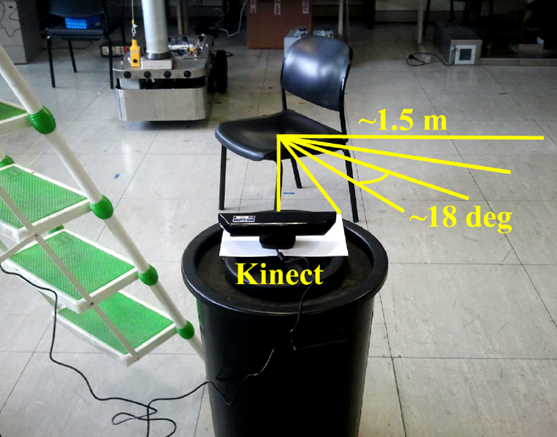
Reference paper: Structure-based object representation and classification in mobile robotics through a Microsoft Kinect, Antonio Sgorbissa, Damiano Verda Robotics And Autonomous Systems (RAS), December 2013
Human localization and mapping
A laser scanner is mounted on a helmet (together with a 6-DOF Inertial Measurement Unit, IMU) to build a map-generation and self-localization application based on wearable sensors.

Reference paper: Human navigation and mapping with a 6DOF IMU and a laser scanner, Marco Baglietto, Antonio Sgorbissa, Damiano Verda, Renato Zaccaria Robotics And Autonomous Systems (RAS), December 2011






